RNase is an organism's "umbrella" that prevents the invasion of foreign RNAs. Such as biological tears, saliva, sweat, and other body fluids secrete RNase. RNases present in the environment are mainly secreted by microorganisms (bacteria and fungi) and consist of tiny compact proteins. It has a disulfide bond in its structure, so it has the natural property of strong stability, is extremely difficult to inactivate, and can quickly restore its conformation after thermal denaturation. In addition, RNase is resistant to heat, acid, and alkali, so it is resistant to many decontamination methods. RNases, especially members of the RNase A family, are tiny, compact proteins. They contain some cysteine residues capable of forming many intramolecular disulfide bonds. Therefore, after returning to room temperature, in the absence of a denaturant, the denatured RNase will restore its natural structure and part of its function. Therefore, RNase retains considerable activity after repeated freeze-thaw cycles, even after autoclaving. The stable nature of these enzymes makes them resistant to numerous decontamination methods, often requiring aggressive chemical methods to eliminate RNases from surfaces and solutions. So how to remove RNase contamination?
1. What is RNase Contamination?
2. How Can RNase Contamination be Avoided at the Source?
3. RNase Inhibitors Prevent Contamination
4. High-quality Murine RNase Inhibitors of YEASEN
5. FAQ
6. Ordering Information
1. What is RNase Contamination?
RNase (Ribonuclease) is a class of nucleases that may catalyze the destruction of RNA into tiny molecules. RNase is found in all cells and tissues of eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms, and even a minimal quantity of RNase contamination in RNA samples can induce total disintegration. The following are the most common causes of RNase contamination in laboratories:
1.1 Exogenous pollution sources
- Experimental consumables, which comprise aqueous solutions used in the experiment, reagents for each component of the reaction system, and pipette tips;
- Experimental ambient contamination (RNase may be found in the air, dust, and most item surfaces);
- the experimenter's skin or saliva.
1.2 Endogenous pollution sources
Endogenous RNase is present in all tissue samples.
2. How Can RNase Contamination be Avoided at the Source?
Widespread RNase contamination makes it difficult to maintain the integrity of RNA samples throughout studies, which might lead to experimenting failure or influence RNA analysis results. As a result, it is vital to minimize RNase pollution at the source, on the one hand, to rigorously limit external RNase corrosion, and on the other hand, to optimize endogenous RNase inhibition.
2.1 Strategy for reducing exogenous RNase contamination:
- The operator is armed to the teeth
RNase contamination from human hands is avoided by wearing gloves during the experiment. After contacting the skin, doorknobs, and regular object surfaces, change gloves.
- Make use of professional reagents and devices
Use RNase-free tips and centrifuge tubes with pipettes designed for RNA manipulation. RNase-free compounds and reagents are used.
- Decide on the operational environment for the experiment
Avoid/obstruct ventilation openings or open windows, and walk less in locations designated as RNase-free zones.
- Additional sites of interest
Other experiments that may generate RNase contamination during RNA extraction and analysis should be avoided.
2.2 The methods for suppressing endogenous RNase activity:
-
Sample preservation
Assume that the RNA is not extracted promptly after tissue collection. To avoid RNA degradation, it is vital to promptly freeze it in a -80 oC environment with liquid nitrogen and conduct studies as soon as feasible.
-
Incorporate inhibitors
To synchronize the shattered cells with inactivated RNase, RNase inhibitors are added to the cell lysate, reducing the activity of RNase produced during cell disruption.
3. RNase inhibitors prevent contamination
RNase inhibitor (also known as RNasin) is a particular RNase inhibitor found in the human placenta that may bind to RNase in a non-covalent bond to create a complex, inactivating RNase and protecting RNA integrity. RNasin is now utilized to preserve RNA during cDNA synthesis, in vitro transcription, in vitro translation, and the extraction and purification of mRNA-protein complexes, as well as to discover unique RNase activities.
4. High-quality Murine RNase Inhibitors of YEASEN
The Murine RNase Inhibitor is a recombinant murine RNase inhibitor expressed in soluble form in Escherichia coli that can inhibit a wide range of RNase (RNase A, B, C) and can be used for RT-PCR/RT-qPCR, solving the problem of RNA degradation in vitro transcription, and inhibiting RNase activity during RNA isolation and purification. RNase Inhibitors are more antioxidant activity and suited for tests with high DTT sensitivity (such as qPCR) than human RNase inhibitors because they do not include two cysteines in human proteins that are particularly susceptible to oxidation.
4.1 Product Features
- All-around RNase inhibition: RNase A, RNase B, and RNase C may all be inhibited.
- Versatile reaction conditions: active at pH 5.0 to 9.0 and temperatures ranging from 25℃ to 60℃, making it ideal for heat-stable reverse transcriptase (55℃ - 60℃).
- Multiple downstream experiments possible: no influence on the activity of SP6, T7, or T3 RNA polymerases, AMV, M-MLV reverse transcriptase, or Taq DNA polymerase.
- Mass-produced goods: a single manufacturing capacity of 2 billion U is helpful to cost management by ensuring product homogeneity, supply stability, and timeliness.
- Batch-to-batch consistency: mature protein expression and purification platform by ISO13485 quality management system, quality control testing by quality requirements to assure product stability between batches.
4.2 Product performance
4.2.1 RNase Inhibitor blocks RNase activity
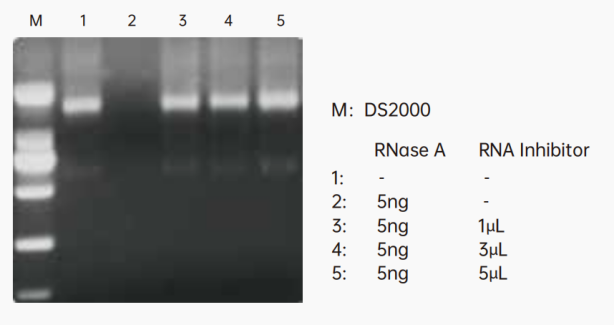
Figure 1. 1 μL RNase inhibitor can effectively inhibit 5 ng RNase, 1 μg HEK cell total RNA electrophoresis results
4.2.2 RNase Inhibitor surpasses foreign products in qPCR testing
The inhibitory impact of the YEASEN and R* Company mouse-derived RNase inhibitors (MRI) was measured using the qPCR technique under identical experimental circumstances, and the RNase inhibitor of the YEASEN Murine source efficiently inhibited RNase A in the system. The impact of inhibition was superior to that of competitors.
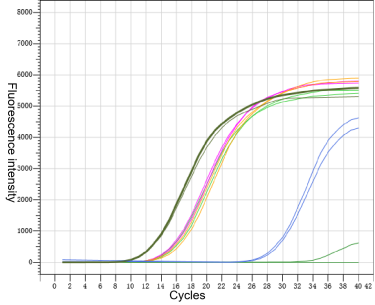
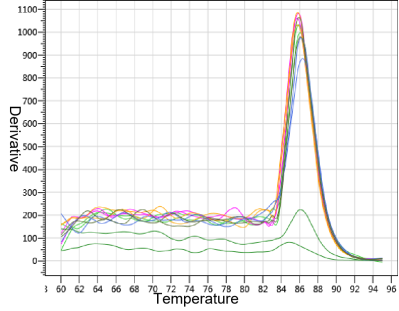
Figure 2. R* MRI RNase inhibition test
Note: The curves in the figure from left to right are: PC (RNA only, no RNase and MRI), 40 U MRI, 30 U MRI, 20 U MRI, 10 U MRI, NC (RNA+RNase, no MRI)
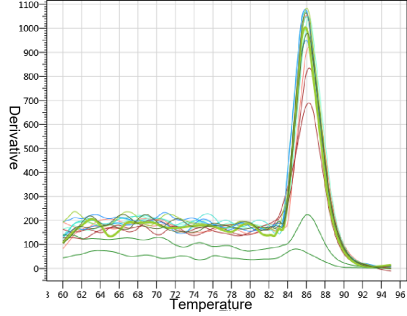
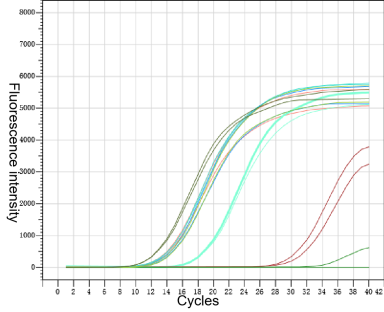
Figure 3. Yeasen MRI RNase inhibition test
Note: The curves in the figure from left to right are: PC (RNA only, no RNase and MRI), 80 U MRI, 60 U MRI, 40 U MRI, 30 U MRI, 20 U MRI, 10 U MRI, NC (RNA+RNase, no MRI)
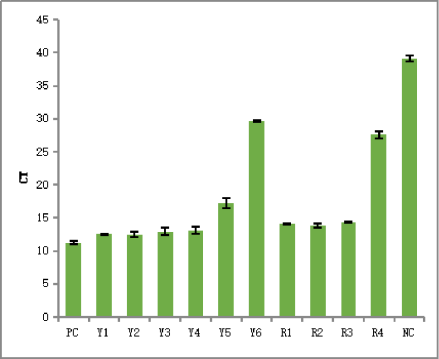
Figure 4. The CT of RT-qPCR results of Yeasen MRI and R* MRI
5. FAQ
1. Will Murine RNase inhibitor have an impact on RT-PCR and qRT-PCR experiments?
A: It will have no effect. Each batch of Murine RNase inbitior is clear of genomic contamination after quality testing and may be used in RT-PCR and qRT-PCR research.
2. What are the precautions while constructing reaction systems using Murine RNase inhibitors?
A: RNase inhibitors can be introduced to a system before additional components that could introduce RNase contamination sources are added.
3. Does the Murine RNase inhibitor have acted as a nucleic acid endonuclease and exonuclease?
A: No nucleic acid endonuclease and exonuclease activity aid in increasing product yield.
6. Ordering Information
Yeasen Biotechnology (Shanghai) Co., Ltd., founded in 2014, is a high-tech enterprise engaged in the R &D and production of tool enzyme raw materials and antigen antibodies. Its products include molecular diagnostic enzymes, proteins, and antibodies used in pharmaceuticals, food safety testing, breeding, justice, and other industries. We are committed to providing customers in the field of life sciences with high-quality products and services. The products that Yeasen can provide are as follows:
Table 1: Products provided by Yeasen
|
Product Positioning |
Product name |
Cat# |
|
RNase inhibitor |
10603ES |
|
|
Hotstart TaqDNA Polymerase |
Hieff Unicon™ Hotstart Direct Taq DNA Polymerase (5 U/μL) (Inquire) |
10717ES |
|
Highly sensitive Bst enzyme |
14402ES |
|
|
Double-Block anti-Taq DNA Polymerase Antibody |
31303ES |
|
|
Reverse Transcriptase for RT-Lamp |
Hifair™ III Reverse Transcriptase (200 U/μL) (Inquire) |
11111ES |
|
Reverse Transcriptase for RT-qPCR |
11300ES |
|
|
heat-labile UDG |
Uracil DNA Glycosylase (UDG/UNG), heat-labile,1 U/μL (Inquire) |
10303ES |
|
dNTP Mix with high purity |
10125ES |
|
|
dUTP with high purity |
dUTP Solution (100 mM) |
10128ES |
Note: All of the above enzymes are available in high-concentration or glycerol-free versions.
Regarding reading:
YEASEN Heat-labile UDG——Easily control aerosol pollution
Murine RNase Inhibitor-Avoiding RNase contamination
Reverse Transcriptase Selection
High-quality isothermal amplification raw materials-Making RT -LAMP more sensitive and faster!