dNTP stands for patterned ribonucleotide triphosphate used in PCR, capable of amplifying a growing DNA strand. In other words, dNTPs in PCR home with complementary DNA strands through hydrogen bonds, and the growing DNA strands are expanded with the help of Taq DNA polymerase. What is the specific application of dNTP in PCR? What are the properties that high-purity dNTPs need to have?
1. What are dNTPs?
2. What is the concentration of dNTP in PCR?
3. What are the required properties of High purity dNTP?
4. Related products and performance
1. What are dNTPs?
Deoxynucleoside triphosphates (dNTPs) are nucleoside triphosphates containing deoxyribose, a chain of nucleotides consisting of ribose, a base, and a phosphate. dNTPs are the essential building blocks of nucleic acid molecules, and as such are necessary components of PCR mixes as no new amplified DNA could be generated without them. The four individual deoxynucleotides which make up a DNA sequence including deoxyadenosine triphosphate (dATP), deoxythymidine triphosphate (dTTP), deoxycytidine triphosphate (dCTP), and deoxyguanosine triphosphate (dGTP). In addition, the quality of dNTPs is also critical for the success of many procedures such as PCR, cDNA synthesis, qPCR, sequencing, cloning, and DNA labeling.
There are four types of dNTP, or deoxynucleotide triphosphate, with each using a different DNA base: adenine (dATP), cytosine (dCTP), guanine (dGTP), and thymine (dTTP). Using dNTP during the extension phase provides single bases ready to go into DNA and double it, like building blocks. Since the purpose of the technique is to synthesize new DNA, dNTP provides nucleotides to the “unzipped” strand using the template of a single side. This turns a single strand of DNA into two, and can continue exponentially as long as reagents remain present until the final hold stage.
2. What is the concentration of dNTP in PCR?
PCR is an in vitro technique of DNA synthesis that is performed to generate multiple copies of a DNA fragment of interest so that it can be visualized under gel electrophoresis. The purpose of PCR is to make a large number of copies of DNA for various downstream applications in DNA sequencing or DNA microarrays. Its components include DNA templates, primers, buffers, and Taq DNA polymerase dNTP. To understand the mechanism of PCR, it is necessary to understand the importance and principle of the components used. dNTP is one of the key components of PCR. The function of dNTPs in PCR is to amplify the growing DNA strand with the help of Taq DNA polymerase and to combine with the complementary DNA strand through hydrogen bonding.
The process of PCR is divided into three temperature-dependent steps: denaturation, annealing, and extension. During the denaturation step, double-stranded DNA is denatured to single-stranded DNA. During the annealing step, the primers bind at the exact location of their complementary sequence, and during the extension step, Taq DNA polymerase adds dNTPs to the growing DNA strand. Once the strands are opened and the primers bind to the single-stranded DNA, Taq DNA polymerase begins its catalytic activity. In the next step, the addition of dNTPs starts, which binds to the P-DNA complex with less affinity if the exact complementary nucleotide is present. Shortly after Taq DNA polymerase holds, hydrogen bonding interactions between complementary bases and dNTPs occur. Here it is not the whole nucleotide at the beginning, but the base (nitrogen base) on the dNTP that decides whether to bind or not. First, if it finds a complementary base (A for T, G for C) on the template ssDNA, it will form a hydrogen bond between them. Three hydrogen bonds between C and G and two hydrogen bonds between A and T are made. Once the hydrogen bond is formed, Taq DNA polymerase complies with the incorporation of the dNTP into the growing DNA strand by forming a phosphodiester bond. Now after the phosphodiester bond is formed, Taq DNA polymerase goes a step further in adding new dNTPs. A phosphodiester bond is formed between the 3'OH of the primer and the 5'P of the dNTP. After hydrogen bonding, Taq DNA polymerase catalyzes the reaction by removing gamma and beta-phosphates from the triphosphates of dNTPs. After the reaction is complete, two pyrophosphates (PPi) are released. But the exact kinetics of dNTPs and Taq polymerase interaction in PCR reactions remains unknown.
These four nucleotides are typically added to the PCR reaction in equimolar amounts for optimal base incorporation. However, in certain situations such as random mutagenesis by PCR, unbalanced dNTP concentrations are intentionally supplied to promote a higher degree of misincorporation by a non-proofreading DNA polymerase. The factor that determines the minimum dNTP concentration is the DNA length and composition of the target sequence. In the PCR reaction, dNTP is generally 50-200 μmol/L. When the final dNTP concentration is greater than 50 mmol/L, it can inhibit the activity of Taq DNA polymerase. The concentrations of the four dNTPs should be equal to reduce misincorporation during amplification due to a lack of one dNTP.
In common PCR applications, the recommended final concentration of each dNTP is usually 0.2 mM. Higher concentrations may be helpful in some cases, especially in the presence of high concentrations of Mg2+, as Mg2+ binds to dNTPs and reduces their rate of incorporation, increasing the non-specific rate. dNTP contains phosphate, which can combine with Mg2+ to reduce the concentration of free Mg2+, so the change in its concentration will affect the effective concentration of Mg2+. Under high concentration DNA and dNTP conditions, the Mg2+ concentration should be adjusted accordingly. Also, the scarcity of dNTPs leads to incomplete PCR products. However, dNTPs exceeding optimal concentrations can inhibit PCR. For efficient incorporation by DNA polymerase, free dNTPs should be present in the reaction at a concentration of no less than 0.01-0.015 mM.
3. What are the required properties of High purity dNTP?
Since its discovery, the polymerase chain reaction is the unmatched tool used in molecular genetic research. dNTP is employed in PCR to expand the growing DNA strand. Even if the quality of dNTP in the system is poor, it will have a negative impact on the final product properties. Yeasen's High purity dNTP is suitable for all kinds of highly sensitive and reproducible DNA synthesis applications.
Yeasen offers ready-to-use GMP-grade nucleotides, sets and mixes, supplied as sodium salts in purified water at pH 7.0. The manufacturing process eliminates impurities and PCR-specific inhibitors, and the dNTPs are specially manufactured for molecular biology applications. The dNTPs are purified with preparative HPLC and possess at least 99% purity. They can be used in PCR, RT-qPCR, LAMP, DNA labeling, and DNA sequencing processes.
Rigorous control standards and state-of-the-art technology ensure the best quality of the product. Each lot of dNTP is tested for various residues (Bacterial DNA, human DNA, DNase, RNase, Endonuclease). The product is stable from batch to batch and suitable for all kinds of highly sensitive and reproducible DNA synthesis applications.
4. Related products and performance
4.1 No Bacterial DNA Residue
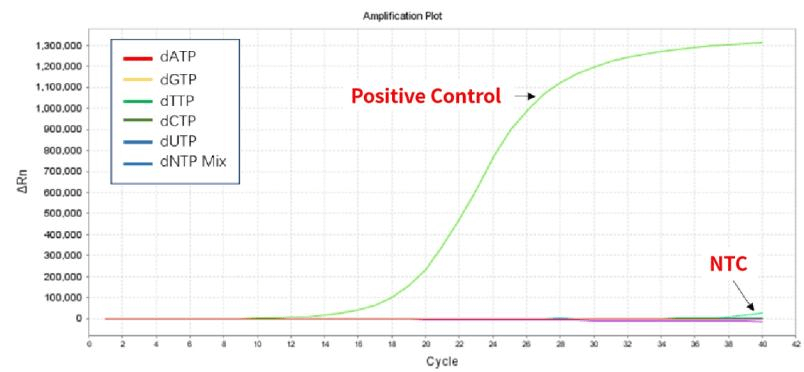
Figure 1. The detection results show that the dNTPs have no bacterial genome residues.
4.2 No human DNA Residue
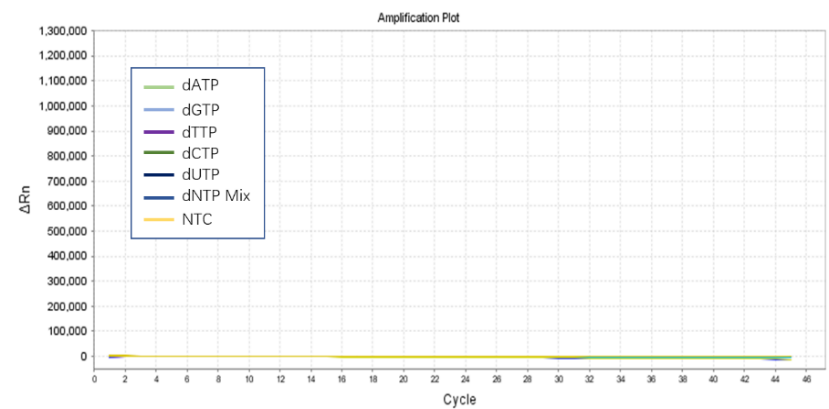
Figure 2. The detection results show that dNTPs have no human genome residues.
4.3 No DNase, RNase, and Endonuclease contamination
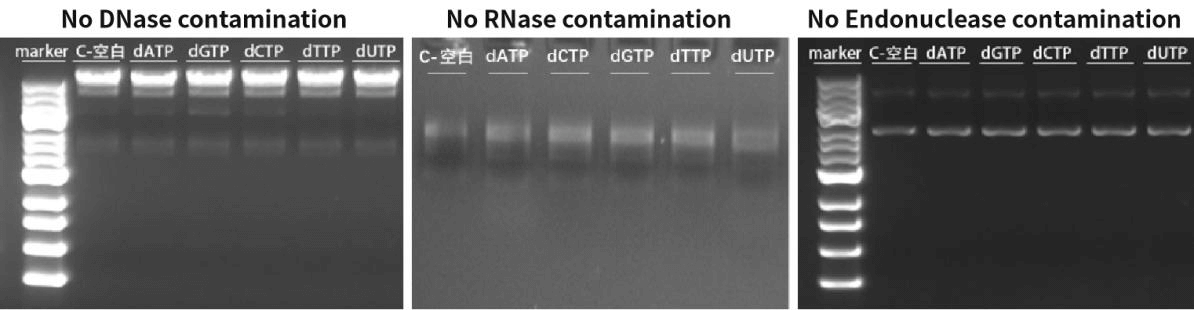
Figure 3. The detection results show that dNTPs have no DNase, RNase, and Endonuclease.
4.4 PCR amplification (20 kb DNA)
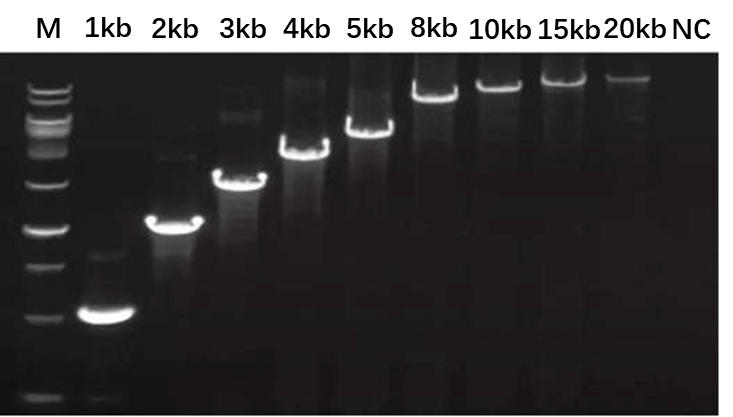
Figure 4. The PCR amplification result is the expected 20 kb product.
4.5 Products information
The products provided by Yeasen are as follows.
Table 1. Products information
| Product Name | SKU | Specifications |
| dNTP Mix (25 mM each) | 10125ES80 | 1 mL |
| 10125ES86 | 25 mL | |
| 10125ES95 | 400 mL | |
| dATP Solution (100 mM) | 10118ES74 | 400 μL |
| 10118ES80 | 1 mL | |
| 10118ES96 | 25 mL | |
| 10118ES97 | 400 mL | |
| dCTP Solution (100 mM) | 10119ES74 | 400 μL |
| 10119ES80 | 1 mL | |
| 10119ES96 | 25 mL | |
| 10119ES97 | 400 mL | |
| dTTP Solution (100 mM) | 10120ES74 | 400 μL |
| 10120ES80 | 1 mL | |
| 10120ES96 | 25 mL | |
| 10120ES97 | 400 mL | |
| dGTP Solution (100 mM) | 10121ES74 | 400 μL |
| 10121ES80 | 1 mL | |
| 10121ES96 | 25 mL | |
| 10121ES97 | 400 mL | |
| dUTP Solution (100 mM) | 10128ES74 | 400 μL |
| 10128ES80 | 1 mL | |
| 10128ES96 | 25 mL | |
| 10128ES97 | 400 mL | |
| dNTP Set Solution (dATP, dCTP, dTTP, dGTP, 100 mM each) | 10122ES74 | 4×400 μL |