T7 High Yield RNA Synthesis Kit
Description
T7 High Yield RNA Synthesis Kit optimizes the transcription reaction system. The kit can synthesize the single-stranded RNA efficiently by using T7 RNA polymerase, the linear double-stranded DNA with the T7 promoter sequence as the template, NTPs as the substrate to control the DNA sequence downstream of the promoter. During transcription, modified nucleotides can be added to the substrate to prepare biotin or dye-labeled RNA.
This kit can synthesize long transcripts and short transcripts, RNA can be produced 100-200 μg with 1 μg of DNA template input. The RNA synthesized by transcription can be used for various downstream applications, such as RNA structure and function research, RNase protection, probe hybridization, RNAi, microinjection, and in vitro translation.

Figure 1: In vitro RNA transcription process
Feature
- Up to 180 μg of RNA per reaction from 1 μg of the control template
- Optimized reaction system for the IVT process
- Decrease the dsRNA production
- Higher RNA integrity and purity
Application
- In vitro RNA synthesis
Components
| Components No. | Name | 10623ES50 (50 T) | 10623ES60 (100 T) | 10623ES70 (500 T) |
| 10623-A | T7 RNA Polymerase Mix | 100 μL | 200 μL | 1 mL |
| 10623-B | 10×Transcription Buffer | 100 μL | 200 μL | 1 mL |
| 10623-C | ATP (100mM) | 100 μL | 200 μL | 1 mL |
| 10623-D | CTP (100mM) | 100 μL | 200 μL | 1 mL |
| 10623-E | GTP (100mM) | 100 μL | 200 μL | 1 mL |
| 10623-F | UTP (100mM) | 100 μL | 200 μL | 1 mL |
| 10623-G | Control DNA Template (500ng/μL) | 10 μL | 20 μL | 100 μL |
Shipping and Storage
Dry ice transportation. Store at -15℃ ~ -25℃, valid for two years.
Figures
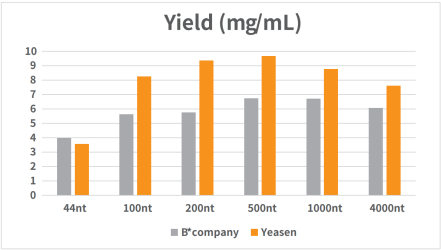
Figure 1. Standard RNA was synthesized in vitro using T7 RNA synthesis kit.
The reaction was incubated in a PCR instrument at 37℃ for 2h and then purified by magnetic beads (Cat#12602). The yield result was analyzed by NanoDrop spectrophotometer as shown in Figure 1.
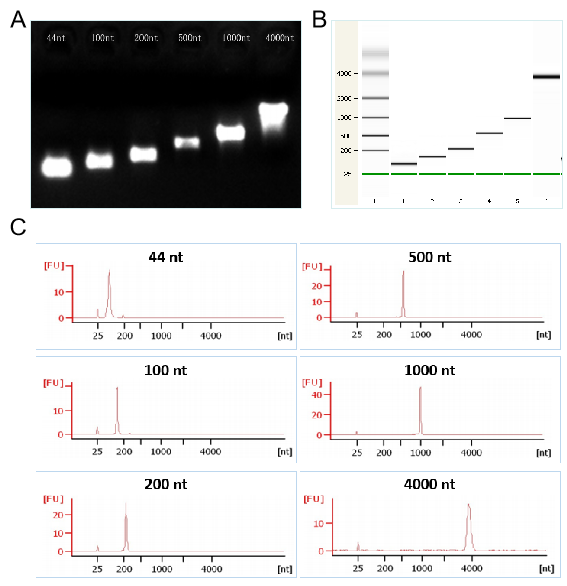
Figures 2. The transcription demonstration of different lengths of RNA by T7 kit respectively in the electrophoretogram (Figures 2A), the capillary electrophoresis diagram (Figures 2B), and the chromatogram (Figures 2C)
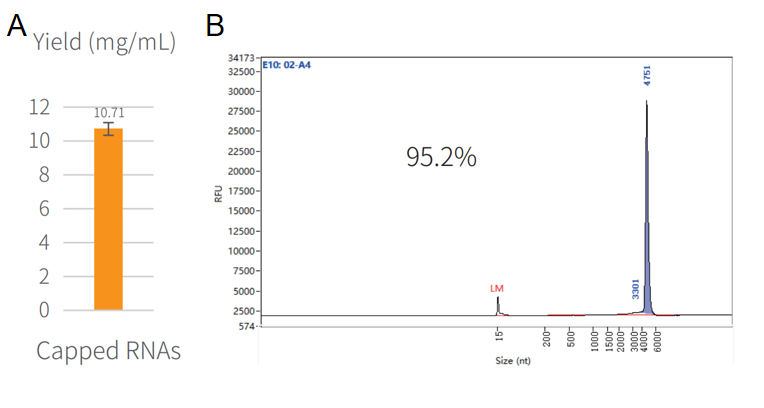
Figure 3. Synthesis of capped RNA in vitro.
The reaction was incubated in PCR instrument at 37℃ for 2h, and then purified by magnetic beads (Cat#12602). The yield result was assayed by NanoDrop spectrophotometer as shown in Figure 3A. The integrity result was analyzed by capillary electrophoresis as shown in Figure 3B.
1. Low transcript yield
The quality of the template is closely related to the yield. If the yield of the experimental group is significantly lower than the control group, the possible reasons are:
① the experimental template contains inhibitory components;
② The template has something wrong.
Suggestions:
① Re-purify the template;
② Determine the template quantification and its integrity;
③ Extend the reaction time;
④ Increase the amount of template input;
⑤ Try other promoters and RNA polymerases.
2. Low yield of short transcripts
A short transcription initiation fragment will inhibit the reaction. When the transcription product is less than 100 nt, extending the reaction time to 4-8 hs or increasing the amount of template to 2 μg will increase RNA yield.
3. RNA transcription length is greater than expected
If the electrophoresis shows that the product band is larger than the expected size, the possible reasons:
①The plasmid template may not be completely linearized;
②The 3' end of the sense strand has a prominent structure;
③The RNA has a secondary structure that is not completely denatured.
Suggestions:
①Check whether the template is completely linearized, and if necessary, perform additional linearization;
②Select a suitable restriction enzyme to avoid 3' overhangs, or use Klenow Fragment /T4 DNA polymerase to complete the transcription before proceeding;
③Use denatured gel to detect RNA products.
4. RNA transcription length is less than expected
If the electrophoresis shows that the product band is smaller than the expected size, the possible reasons:
①The template contains a termination sequence similar to T7 RNA polymerase;
②The GC content in the template is high.
Suggestions:
①Lower the reaction temperature (for example, 30°C). Sometimes lowering the temperature can increase the transcription length, but it will reduce the yield. Or try different RNA polymerases for transcription;
②If the template GC content is high, use 42℃ to transcript, or add SSB to increase the yield and transcription length.
5. Electrophoresis tailing of transcription products
There is a tailing phenomenon during electrophoresis.
Possible reasons:
①Contaminated by RNase during experimental operation;
②Contaminated DNA template by RNase.
Suggestions:
①Use RNase-free pipette tips and EP tubes, wear disposable latex gloves and masks, and all reagents are prepared with RNase free H2O.
②Re-purify the template DNA.
[1] Dong Z, Zheng N, Hu C, et al. Nosema bombycis microRNA-like RNA 8 (Nb-milR8) Increases Fungal Pathogenicity by Modulating BmPEX16 Gene Expression in Its Host, Bombyx mori. Microbiol Spectr. 2021;9(2):e0104821. doi:10.1128/Spectrum.01048-21(IF:7.171)
[2] Wang X, Tang S, Ye S, et al. Ultrasensitive quantitation of circulating miR-195-5p with triple strand displacement amplification cascade. Talanta. 2022;242:123300. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123300(IF:6.057)
Catalog No.:*
Name*
phone Number:*
Lot:*
Email*
Country:*
Company/Institute:*

